what is the OSI model ?
- OSI model stands for Open Systems Interconnection Model.
- This model focuses on providing a visual design of how each communications layer is built on top of the other
- The open systems interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual model created by the International Organization for Standardization
- which enables diverse communication systems to communicate using standard protocols.
- OSI 7-layer model is still widely used, as it helps how networks operate, and helps isolate and troubleshoot networking problems.
Layers of OSI Model
There is total 7-layers in the OSI Model .
- Application
- Presentation
- Session
- Transport
- Network
- Data-Link
- Physical
How we can graphically represent the OSI Model ?
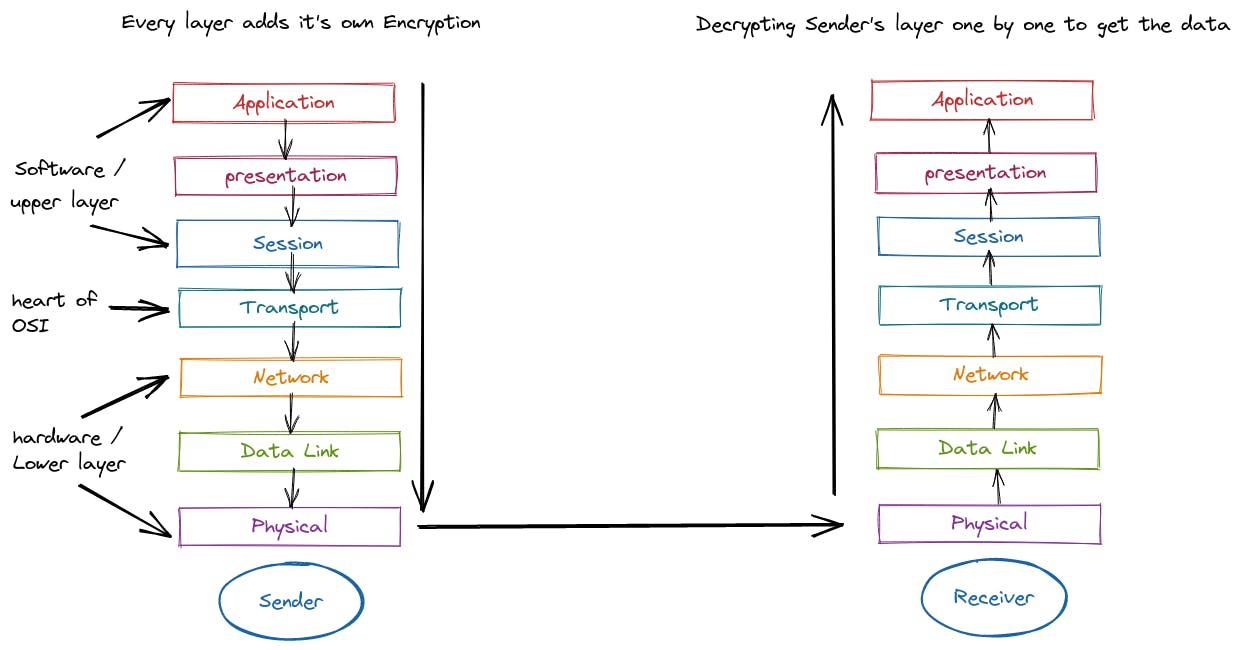
Let's learn how each layers communicates with each other
Application Layer
- The Application layer enables the user to interact with the application or network whenever the user elects to read messages, transfer files or perform other network-related tasks.
- Only the users Interact with Application layer.
- Applications like browsers,Skype Messenger apps.
Presentation Layer
- Presentation Layer takes data from the application layer and converts it into the machine/binary Language.
- Presentation Layer also provides Abstraction.
- The Encryption takes place at presentation layer.
- Presentation layer Compares the data before it transfers the data to session layer.
Session Layer
- This layer is responsible for the establishment of connection, maintenance of sessions, authentication, and also ensures security.
- It enables sending and receiving data followed by termination of the connected session.
- The session layer allows two systems to start communication with each other in half-duplex or full-duplex.
Transport Layer
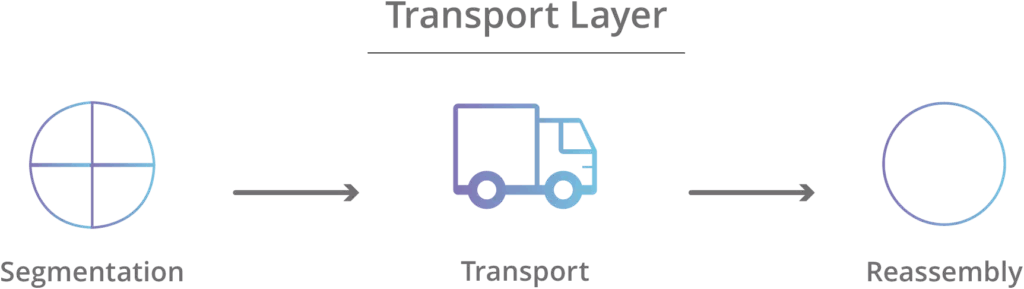
- The transport layer provides services to the application layer and takes services from the network layer.
- Transport layer controls the amount of data going to be transported.
- In Transport layer
Error controltakes place. - At sender’s side: Transport layer receives the formatted data from the upper layers and performs
Segmentation.
Transport Layer provides two types of services.
- Connection-Oriented Service: In this type of transmission, the receiving device sends an acknowledgement, back to the source after a packet or group of packets is received. This type of transmission is reliable and secure.
- Connection-less Service : In this type of transmission, the receiver does not acknowledge receipt of a packet. Connection-less Service allows for much faster communication between devices.
Network Layer
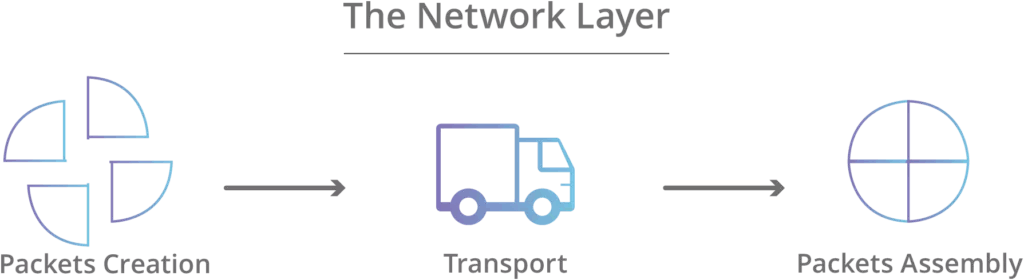
- The network layer works for the transmission of data from one host to the other located in different networks.
- it provides a logical address and makes an IP packet.
- It also takes care of packet routing and Load balancing.
Segment in Network layer is referred to as Packet.
Data-Link Layer
- The data link layer is responsible for the node-to-node delivery of the message.
- The main function of this layer is to make sure data transfer is error-free from one node to another, over the physical layer.
- Data-Link Layer assigns physical / MAC address to the
data packet to frame. Packet in Data Link layer is referred to as Frame.Data-Link performs functions
- It allow all the upper layer OSI Model to access frame which are going to transferred by data-link layer.
- It Controls how the data is placed and received from the media's using MAC(Media Access Control).
- Data link layer provides the mechanism of error control in which it detects and re-transmits damaged or lost frames.
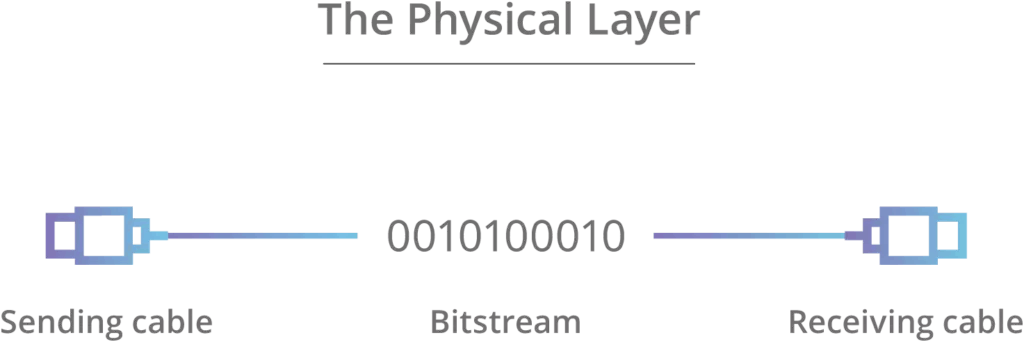
Physical Layer
- The lowest layer of the OSI reference model is the physical layer.
- Physical Layer contains the hard wares like Hub, Repeater, Modem, Cables and it transmits electrical signal.
- It is responsible for transmitting individual bits from one node to the another.